Schedule a service call online to ensure that your AC is ready for the hot summer ahead!
Air conditioners are complex machines with many moving parts, but the basic process is simple: remove heat from the air through evaporation. When a liquid evaporates, it absorbs heat and leaves the surrounding area cooler. The cyclical process of an air conditioner repeats, ensuring your home is always cool and comfortable.The following infographic explains the mechanics behind the machines that create a climate haven in our homes.
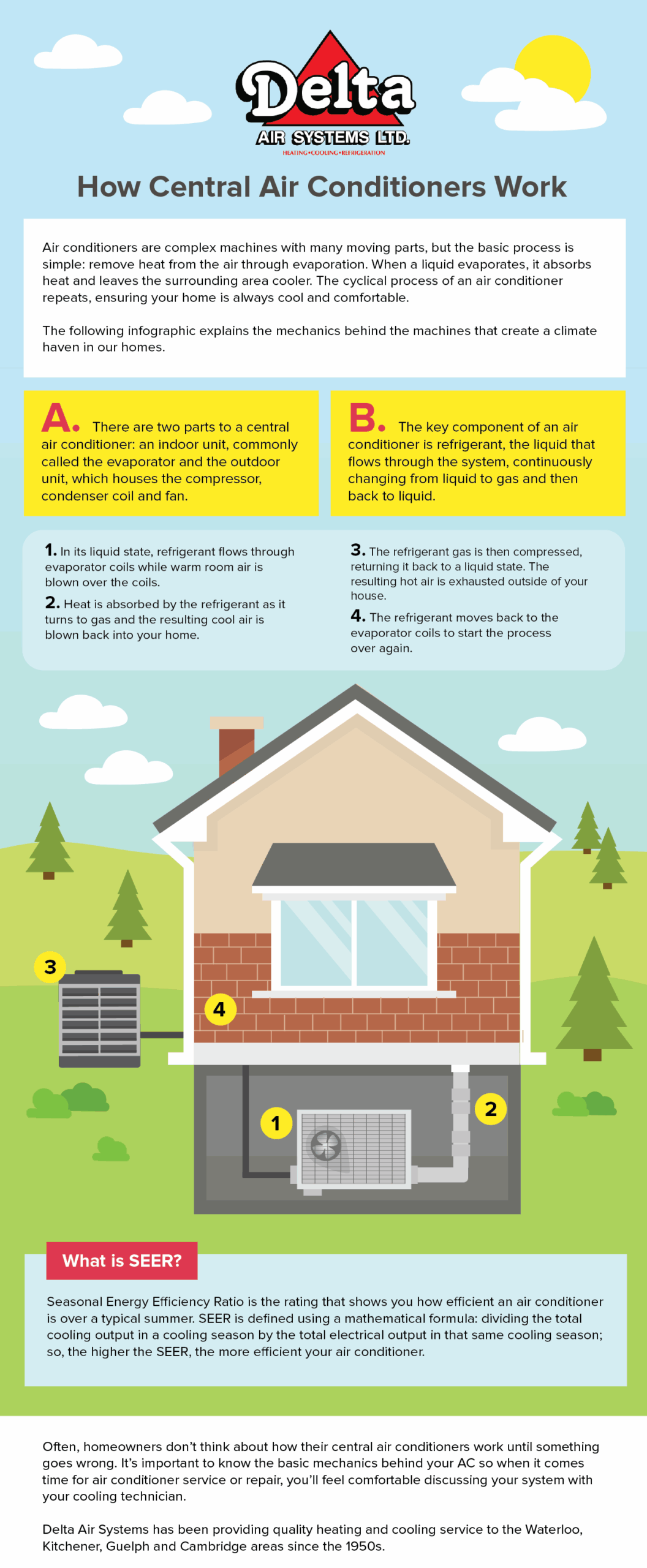
INFOGRAPHIC COPY: There are two parts to a central air conditioner: an indoor unit, commonly called the evaporator and the outdoor unit, which houses the compressor, condenser coil and fan.The key component of an air conditioner is a refrigerant, the liquid that flows through the system, continuously changing from liquid to gas and then back to liquid.1. In its liquid state, the refrigerant flows through evaporator coils while warm room air is blown over the coils.2. Heat is absorbed by the refrigerant as it turns to gas and the resulting cool air is blown back into your home.3. The refrigerant gas is then compressed, returning it back to a liquid state. The resulting hot air is exhausted outside of your house.4. The refrigerant moves back to the evaporator coils to start the process over again.What is SEER?Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio is the rating that shows you how efficient an air conditioner is over a typical summer. SEER is defined using a mathematical formula: dividing the total cooling output in a cooling season by the total electrical output in that same cooling season; so, the higher the SEER, the more efficient your air conditioner.